The so-called "robotic automation" refers to a mode of realizing industrial automated production with multi-joint industrial robots as the center. Compared with traditional non-standard automated production equipment, it has its own unique characteristics. Understanding these characteristics and giving full play to the advantages of robots are what non-standard automation engineers have always wanted to know.
Analysis and understanding of customer needs, analysis of product production processes, decomposition of automated actions, and accumulation of engineer design experience. The accumulation of experience is not a one-day job, which determines the high labor cost of non-standard equipment design.But this also brings irreplaceable competitive advantages to non-standard automation companies.
Robotic automation has brought about a significant reduction in the workload of non-standard design. Only by reasonably designing the gripper, dress, and some relatively standard peripheral equipment can complex automation functions be completed. This enables enterprises to complete the design, installation, and commissioning of more production lines at the same labor cost, and achieve the scale expansion of enterprises. Engineers with non-standard design experience should understand the characteristics of robotic automation and the application characteristics of the robot itself, so that they can better and faster transition to the application thinking of robotic automation.
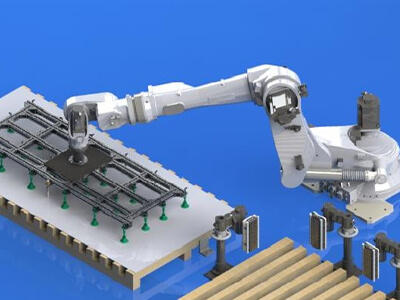
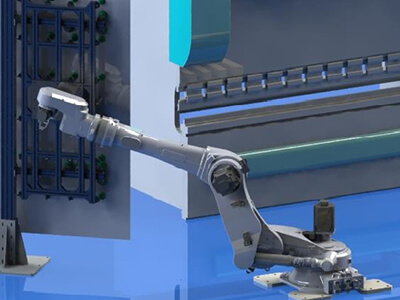
General process of robotic automation planning
Demand analysis >> production process analysis >> clarify robot function modules (what actions the robot completes) >> clarify standard peripheral configuration >> solution layout >> gripper concept >> solution simulation >> standard peripheral concept >> beat simulation >> detailed design. The above is the general design process of robot automation. It can be seen that it has more simulation links than non-standard design, because the robot is a standard device that can move. The range of motion (accessibility), load and motion capacity (beat) are its core capabilities, and the selection of the robot depends on this.
A good grasp of the simulation process can greatly reduce the complexity of design work and reduce dependence on non-standard design experience.
Robot automation focuses the design work on the design of robot grippers, and gripper design relies more on selecting appropriate pneumatic and electric components for the fingers. Design engineers only need to design the connection structure reasonably. Engineers used to spend a lot of energy designing mechanical structures and checking strength and rigidity, but now they only need to select reasonable action components to realize functions, and other actions are handed over to simulation engineers to complete. The planning of beats is also handed over to robot simulation engineers, and even the accessibility layout can be proposed by robot engineers. Reference values help design engineers determine the optimal layout.
The volume of design drawings for robotic automation workstations is only 10% to 20% of the volume of non-standard design drawings. This alone is enough to evaluate the biggest difference between the two.
Planning automation with robots at the center
The robot itself is a standard device, and stability is its biggest advantage. Just like cylinders and reduction motors, they can be successfully integrated into automation design without understanding their internal structure. The disadvantage is that the cost of robots is more expensive than non-standard equipment. However, by reasonably allocating the action rhythm, one robot may complete the functions of 2, 3 or even more non-standard design special equipment. Replacing the cost of multiple special machines with one robot will not only not make the overall project cost much less expensive, but also non-standard design will cost more debugging labor during the installation and commissioning stages, and there will be more adjustment and optimization task labor during the trial operation stage. According to statistics, the labor cost of design, installation, and commissioning of a project dominated by non-standard automation can account for 25% of the project cost, while the labor cost of a project dominated by robot automation can be reduced by 1/2 or even 2/3.
The stability of robots is much better than non-standard equipment that relies on the experience of specific design engineers. In the later stages of the project (debugging, optimization, and transformation), the number of people required to be on site is greatly reduced, and the experienced engineers saved can have more time to devote to the design of new projects.
Transition from non-standard automation design to robotic automation expert
Robotic automation requires experts who have a deep understanding of what robots can do and what they are good at. It is not difficult for experienced non-standard design engineers to become such experts. However, they need to break the habitual thinking of implementing automation solutions, understand robots, and understand and analyze robot application examples.
Start by getting familiar with and understanding what the robot can do and what it is good at, and prioritize analyzing and thinking about how to use the robot to complete more actions and functions;
Break the mindset that everything can be achieved with mechanical structures; every joint movement of the robot can be utilized, not just the end flange.
Imagine that a suction cup installed on a robot arm can also handle workpieces and accessories;
Suction, clamping, clamping and pushing can all be designed into the gripper, and you should be familiar with and understand the standard finger parts designed specifically for robot automation;
Visit as many examples of robotics applications as possible.Understand the combined application of robots and industrial vision systems, and understand flexible applications such as visual tracking, linear tracking, and 3D vision. Reducing fixture positioning and accompanying fixtures in the design, and simplifying the structure of the conveyor are all effective means to optimize project costs.


Sobre nós
A Durmapress é especializada na conceção, fabrico e venda de vários equipamentos de processamento de metal, incluindo máquinas de dobragem, tesouras, punções, máquinas de corte a laser, etc. A empresa foi fundada em 2000. Com anos de experiência e acumulação de tecnologia. DurmaPress tornou-se uma das marcas bem conhecidas na indústria de máquinas de processamento de metal da China.
Contactar-nos
Publicações recentes
Categorias
Siga-nos
Novo vídeo semanal
Contacte-nos para mais informações
Se tiver alguma informação sobre os nossos produtos, contacte-nos e responderemos no prazo de 24 horas.



-300x169.jpg)

