-300x169.jpg)
This article will start with three aspects of laser cutting materials: laser cutting of carbon steel, laser cutting of stainless steel, and stainless steel high-pressure nitrogen cutting, and summarize the various defects and solutions of laser cutting.
Defects and solutions of laser cutting carbon steel
1.Defect type: nozzle perforation is eccentric, cutting is not round
.jpg)
During the laser cutting process, if there are defects such as eccentric perforation or irregular cutting circle, the possible reasons include misalignment of the lens center, blockage of the nozzle hole or non-circular hole shape, or deviation of the laser light path. Such problems usually lead to unstable cutting starting point and affect the overall cutting quality.
In order to solve the above problems, it is necessary to check whether the center position of the lens is correct, confirm whether the nozzle hole is clean and regular in shape, and also check whether the entire light path is offset and correct it by re-targeting to ensure the accuracy of the laser path.
2.Defect type: Poor perforation edge, obvious cracks or burrs
.jpg)
Another common defect is cracks and burrs on the edge of the perforation, or even deformation of the hole. These problems may be caused by the lead-in wire being too long or the lead-in method being improper, resulting in an unstable cutting start process. In addition, if the selected wire type is inappropriate, the perforation time is too long, or there is too much heat input during the cutting process, it will also aggravate edge erosion or burrs.
For such situations, the length and method of the lead-in wire should be optimized to ensure its rationality, and the cutting wire type that matches the material and process should be selected. The perforation time should be controlled within two seconds, and the duty cycle during cutting should be appropriately reduced by 2% to 3% each time to reduce heat accumulation and improve cutting quality.
3.Defect type: burnt cutting edge, obvious dross
.jpg)
During the laser cutting process, if the cutting edge is burnt, the burrs are severe, or the slag is obvious, the possible reasons include too high cutting gas pressure, too high laser focus position, too high laser power setting, or poor quality of the material used. These factors will cause heat to accumulate at the edge of the cut, resulting in an uneven cut surface or even ablation.
To solve such problems, you can try to appropriately reduce the pressure of the cutting gas, each adjustment within 0.1 bar, and check the focus position to ensure that it is in the best focus state. If necessary, the laser power setting should also be reduced, and the performance of the material itself should be checked to confirm whether it is suitable for the current process parameters.
4.Defect type: incomplete cutting, intermittent edges
.jpg)
If the cutting is not thorough, the edge is discontinuous, or the slit is interrupted, it is usually due to insufficient laser power, too fast cutting speed, or insufficient gas pressure. This problem will cause the laser to not completely penetrate the material during the cutting process, resulting in incomplete slits or interruptions.
To deal with this situation, you can increase the energy density by increasing the laser power, or appropriately reduce the cutting speed to extend the action time of the laser and the material. At the same time, increasing the pressure of the auxiliary gas can also help remove slag and improve the cutting effect, thereby obtaining a smoother cutting edge.
5.Defect type: Rough cutting surface, uneven edges
.jpg)
When the cut part has a rough surface, uneven texture or even edge deformation, it may be due to excessive local heat accumulation during the cutting process, causing the material to deform due to heat, or there is a problem with the quality of the material itself, resulting in unstable cutting effect and rough cut surface.
To solve this problem, the heat distribution can be optimized by adjusting the cutting order to avoid heat concentration in local areas. It is also recommended to replace materials with better quality and stronger adaptability to improve the overall quality and consistency of the cutting surface.
6.Defect type: obvious ripples on the cutting surface
.jpg)
If regular or irregular wavy lines appear on the edge of the cut piece, it is usually caused by too high gas pressure or too fast cutting speed. This situation will make it impossible to blow off the slag in time, shorten the laser action time, and ultimately affect the smoothness of the cut surface.
To avoid such problems, the auxiliary gas pressure can be appropriately reduced. It is recommended to adjust the range to 0.1~0.2 bar each time. At the same time, the cutting speed should also be reduced to make the laser energy more effective, thereby improving the flatness of the cut surface and reducing the generation of ripples.
Defects of laser cutting and their treatment methods
1. The bottom surface has melting points and burrs

When melting points and burrs appear on the bottom of the cut piece, it is mostly because the speed is too fast, the air pressure is too low, and the focus is below the surface, which directly affects the cutting and forming effect. When adjusting, you need to reduce the speed, increase the air pressure, and move the focus to the upper part of the surface.
2.Localized overheating

Partial overburning of the cut part is usually caused by impurities in the plate, uneven surface material, and excessive air pressure, which leads to local overburning. It is necessary to check the quality of the plate and adjust the air pressure reasonably to improve the overburning problem.
3.Interface overheating

Overburning of the cutting interface is often caused by not using the arc lead-in in a standardized manner (the recommended R is 1.5 mm, and the radius of the straight line and the circle are equal). When processing, it is necessary to check the lead-in method and adjust the arc parameters according to the standard. If the back side is overburned, it is necessary to leave material for processing to ensure the quality of the interface cutting.
4.Hard burrs on all 4 sides

The burrs on the four sides of the cutting piece are mostly caused by slow speed, low air pressure, and the focus is located on the upper surface, resulting in an imbalance between the cutting energy and the airflow. When adjusting, you need to increase the speed, increase the air pressure, and move the focus below the surface to restore the cutting parameters to a reasonable match and reduce the burrs.
5.There are hard burrs locally

The presence of hard burrs in some parts of the cut part indicates that the cutting parameters are not accurately adapted to the local area. You need to refer to the adjustment logic of the 4-side hard burrs, and carefully adjust the speed, air pressure, focus position and other parameters. Through precise debugging, the cutting conditions are matched with the material characteristics to improve the local hard burr problem.
6.Soft burrs on all 4 sides

The main reason for soft burrs on the four sides of the cut piece is that the speed is too fast and the focus deviates below the surface, resulting in insufficient laser action time and affected energy concentration. When processing, the cutting speed needs to be reduced to allow the laser energy to fully act, and the focus position needs to be corrected to a reasonable depth to reduce the generation of soft burrs.
7.Impure oxygen (less than 99.6)

When the oxygen is impure, even if the power is high, there will still be slag on the back of the cutting, accompanied by the phenomenon that the gas pressure exceeds the normal standard and the speed cannot be increased. This is because the oxygen purity is insufficient, which cannot effectively support combustion and remove slag, resulting in an imbalance of cutting process parameters, affecting cutting quality and efficiency.
8.Impure nitrogen (less than 99.6)

Impure nitrogen will make the cut surface blue or purple (normally it should be white), and will also cause slag on the back of the cut. In addition, it is not recommended to use it for a long time because it will contaminate the focusing lens. This is because the nitrogen purity is insufficient and the cutting environment cannot be maintained stably, which not only affects the cooling and slag removal effect, but also causes damage to the equipment components.
Defects in Stainless Steel Cutting
.jpg)
.jpg)
Quality problems in stainless steel cutting are mainly caused by nozzle damage and insufficient observation during equipment operation. Prevention requires increased vigilance for wearing parts (such as nozzles), inspection and replacement; at the same time, strengthen observation during equipment operation, timely discover and handle abnormalities, and ensure stable cutting quality.
.jpg)
.jpg)
Quality problems in stainless steel cutting are caused by excessive cutting speed, damaged cutting parts, and non-vertical gun heads. Prevention requires controlling the cutting speed, strengthening the inspection and replacement of vulnerable parts, and increasing observation during equipment operation, implementing equipment inspections, and ensuring normal cutting.
.jpg)
.jpg)
The defect of missing 5mm matrix from the outer circle often occurs at the end of the part cutting track or the starting point of another part. It is caused by insufficient support of the part, which tilts on the support bed and interferes with the cutting track. Prevention needs to start from two aspects. First, fully consider the safety of the cutting track during programming to reduce the risk of accidents; second, the operator should strengthen observation during the cutting process and clean up the tilted parts in time to avoid interference problems.
.jpg)
The plate undergoes stress deformation during processing, causing the secondary cutting points that should have overlapped in the program to deviate during actual cutting. To prevent this, the program needs to be modified appropriately according to the plate deformation, and the cutting seams should be overlapped as much as possible (if the deformation is large and affects the dimensional accuracy, there is currently no better solution).
.jpg)
The plate deforms due to stress during processing, resulting in deviations in the actual cutting of the overlapping secondary cutting points in the program. For prevention, when processing plates with an aspect ratio greater than 1:10, try to use the whole plate for processing, or first spot weld the narrow plate and then cut it in sections to reduce the deviation caused by deformation.
.jpg)
.jpg)
Cutting problems are caused by equipment abnormalities. The cause is equipment abnormalities. Prevention requires summarizing equipment abnormalities so that they can be specifically eliminated and similar situations can be avoided in subsequent processing.
.jpg)
Cutting anomalies are caused by programming problems. This defect is caused by deficiencies in the programming process. To prevent it, it is necessary to fully consider the utilization rate of residual materials during program design and avoid such problems by optimizing the programming solution.
.jpg)
The causes of large burrs are complex. After eliminating the influence of parameters such as cutting speed, it is mostly caused by abnormal spare parts (such as lenses, nozzles), or the equipment needs internal and external optical path maintenance. Prevention requires increasing the frequency of random inspections to avoid batch problems, and regularly implementing optical path maintenance work.
.jpg)
The cause of abnormal perforation defects has not been fully identified. It is speculated that it may be related to the conditions and reliability of the equipment's internal program for determining whether perforation is complete. Prevention requires more observation of equipment operation, recording and retaining original data to provide support for subsequent maintenance and improvement.
.jpg)
.jpg)
Burning of the edge of the part. This defect is caused by spare parts problems and slag accumulation on the water bed, which makes it impossible to drain the slag produced by cutting. It accumulates on the lower surface of the part and burns the edge of the product (only occurs when cutting thick plates). Prevention requires strengthening the control of vulnerable spare parts, timely detection and replacement; at the same time, clean the water bed in time. If a problem is found, immediately interrupt the processing to avoid burns.
.jpg)
The cutting node is abnormal. This defect is caused by programming problems. Prevention requires adjusting the lead-in and lead-out methods to reduce node protrusion, but this method has the potential risk of increasing local injuries, which needs to be weighed in actual operation.
.jpg)
.jpg)
Cutting defects are caused by on-site operational errors. This defect is caused by errors in the operation process. To prevent it, it is necessary to strengthen the skills training of operators and strengthen the awareness of product quality protection to reduce the occurrence of such defects from the operational level.
.jpg)
Cutting size deviation, stress deformation of the plate during processing, or falling into the depression of the support plate will cause the program to cut the next specification on the finished product, resulting in actual size deviation. Prevention requires strengthening the control of the processing process, timely detection of abnormal conditions, and avoidance of losses.
.jpg)
.jpg)
The cutting surface is abnormal. This problem is caused by the instability of the sand supply system and spare parts problems. At present, prevention is difficult because the abnormality cannot be discovered in time. In the future, it is necessary to strengthen the stability inspection of the sand supply system, regularly check the status of spare parts, and identify potential risks before problems occur as much as possible.
.jpg)
Cutting defects are caused by lax trial operation before processing. The reason is that the trial operation before processing is not strictly implemented. Prevention requires strengthening skill training, standardizing operating procedures, and clarifying that effective trial operation must be carried out before cutting. Through rigorous trial operation, potential problems can be checked to avoid cutting defects caused by omissions in the preparation process.
.jpg)
The cutting path is offset because the operator neglects to observe and fails to avoid obstacles on the processing route in time, causing the gun head to hit the fixed wood, which eventually causes the cutting line to deviate. Prevention requires strengthening skill training, standardizing operating procedures, strictly implementing effective trial runs before cutting, and checking obstacles in the processing route in advance to avoid cutting abnormalities caused by operational omissions.
.jpg)
Cutting slag rebound residue, due to the rebound of slag residue during cutting, causes problems. Prevention requires regular cleaning of accumulated slag on the support plate to reduce the slag accumulation area, which can effectively avoid the cutting slag rebound phenomenon.
.jpg)
The cutting surface is abnormal, because the cutting was not completely through, and the subsequent re-cutting caused problems. Prevention requires setting appropriate cutting parameters before cutting. It is recommended to use the remaining board of the same specification for trial cutting, and determine the precise parameters through trial cutting to avoid the situation of incomplete cutting and re-cutting.
.jpg)
The board surface is polluted because there are many footprints on the board surface and the quality protection awareness is weak. Prevention requires strengthening the "three preventions" publicity, improving the quality protection awareness of the board, and placing signs to remind operators that hard-to-clean stains can be erased with an eraser.
.jpg)
.jpg)
The edge of the parts is damaged. When cleaning the parts, due to negligence, the parts collide with each other without paying attention, which eventually leads to edge damage. Prevention requires strengthening quality promotion, improving the operators' awareness of protecting the quality of finished products, standardizing cleaning operations, and avoiding damage caused by parts collision.
Common Problems of Stainless Steel High Pressure Nitrogen Cutting and Laser Cutting:Carbon steel: cut with o2
1. Small regular burrs on both sides of the cut
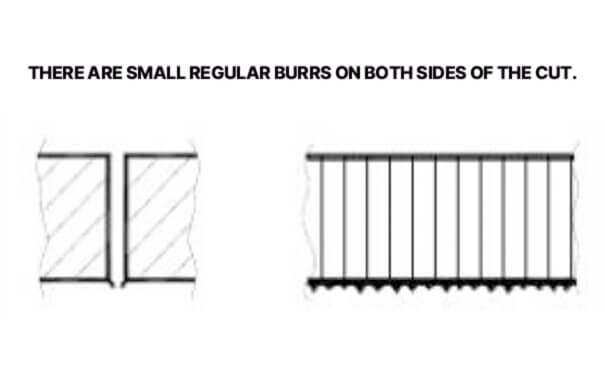
Small regular burrs on both sides of the slit are caused by the focus position being too low and the cutting speed being too high. To solve this problem, you need to increase the focus position and reduce the cutting speed to make the parameters adapt to the cutting requirements.
2. Long irregular burrs on both sides of the cut
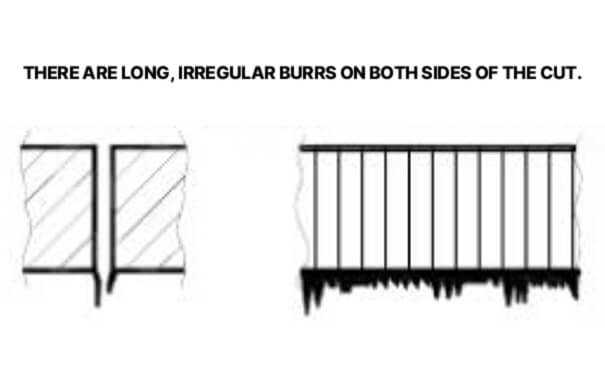
Long irregular burrs on both sides of the slit are caused by low cutting speed, high focus position, low gas pressure or overheated material. Solutions include increasing cutting speed, lowering focus position, increasing gas pressure, and cooling if the material is overheated.
3. Only long linear irregular burrs on both sides of the cut
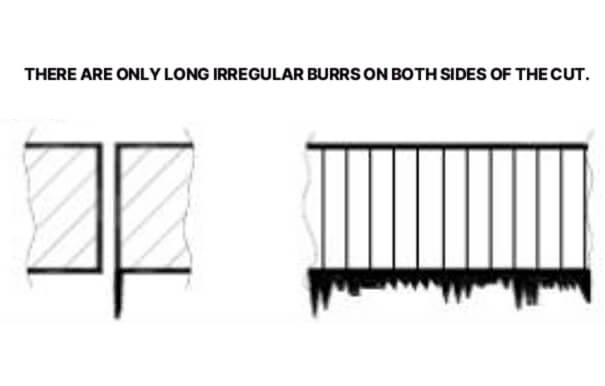
There are only long irregular burrs on both sides of the slit, which are caused by the nozzle not being in the center, the focus position being too high, the gas pressure being low or the cutting speed being low. When dealing with this problem, you need to adjust the nozzle to the center position, lower the focus height, increase the gas pressure, and increase the cutting speed.
4. Cutting edge yellow
Caused by impure nitrogen (containing oxygen). To solve this problem, you need to use high-purity nitrogen to ensure gas purity and avoid discoloration of the cutting edge caused by oxidation.
5. Plasma gas is generated and the workpiece cannot be cut through
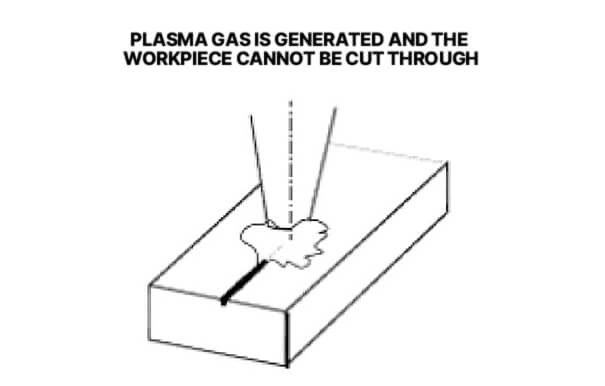
This is caused by too high cutting speed, insufficient laser power, and too low focus position. To solve this problem, you need to reduce the cutting speed, increase the laser power, and at the same time increase the focus position so that the parameters match the cutting requirements.
6. Beam interruption
Caused by too high cutting speed, low laser power and low focus position. The solution is to reduce the cutting speed, increase the laser power, increase the focus position and ensure stable beam output.
7. Rough cut
Caused by nozzle damage or lens contamination. To solve the problem, you need to replace the damaged nozzle and clean the contaminated lens. If the problem still cannot be improved after cleaning the lens, replace the lens directly to ensure the quality of the cutting surface.
Summary of causes and solutions for laser cutting defects
1. No burrs, consistent pulling line

This is the ideal cutting state, because the power and feed rate are adapted. No additional processing is required, just maintain the current appropriate power and feed rate.
2. Bottom leader line offset and bottom cutout wider
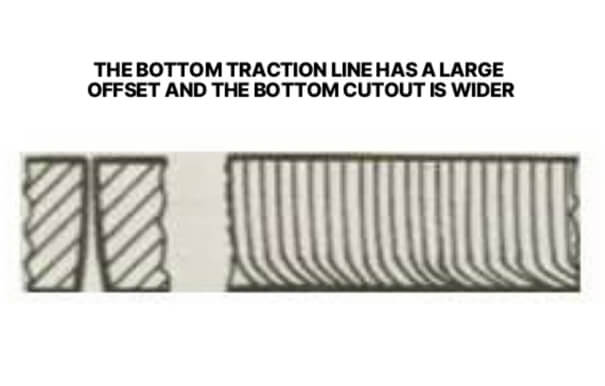
This is caused by too high feed rate, insufficient laser power, low air pressure or too high focus. To solve this problem, you need to reduce the feed rate, increase the laser power, increase the air pressure, and lower the focus height to make the parameters match the cutting requirements.
3. The burrs on the bottom surface are like slag, which are easy to remove in the form of drops.
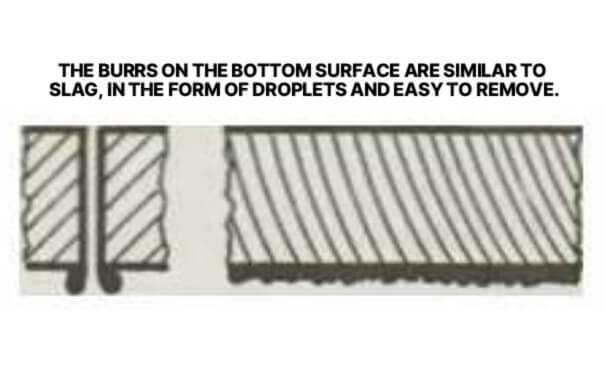
Caused by high feed rate, low air pressure or high focus. The treatment method is to reduce the feed rate, increase the air pressure, lower the focus, and optimize the cutting conditions to reduce this type of burr.
4. Connected metal burrs can be removed as one piece

This is caused by the focus being too high. To solve this problem, you need to lower the focus position, adjust the cutting focus to a suitable height, improve the cutting quality, and eliminate this type of burr.
5. Metal burrs on the bottom surface are difficult to remove
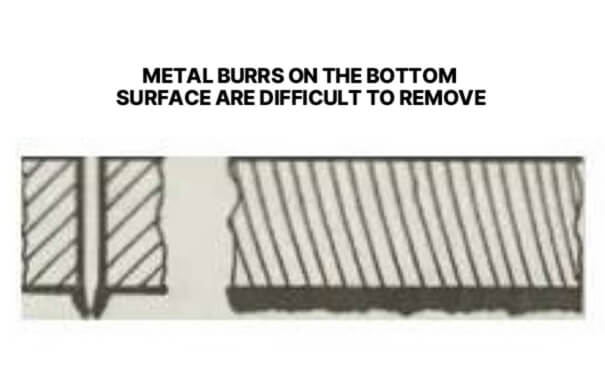
Possible causes: feed rate too high, air pressure too low, impure gas, focus too high. Solution: reduce feed rate, increase air pressure, use purer gas, lower focus.
6. Burrs only on one side
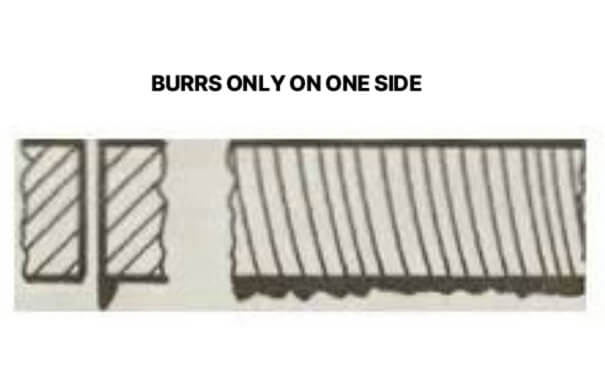
Possible causes: incorrect nozzle alignment, defective nozzle opening. Solution: Align the nozzle, replace defective nozzle.
7. Material is discharged from above
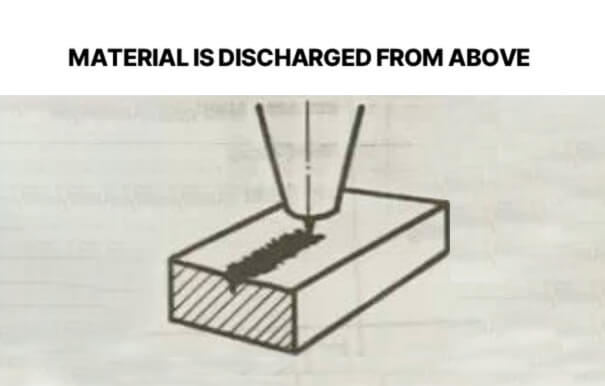
Treatment measures: Press the pause button immediately to prevent slag from splashing onto the focusing lens. Then increase the laser power and reduce the feed rate.
8.Inclined surface cutting, two sides good, two sides bad

Possible reasons: The total reflector is not suitable, is not installed correctly or is defective; the total reflector is installed in the position of the deflection mirror. Solution: Check the total reflector; check the deflection mirror.
9.Blue plasma, workpiece not cut through
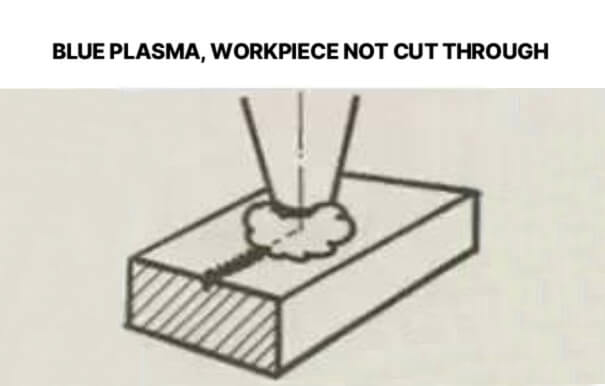
Possible causes: Wrong processing gas; Feed rate too high; Power too low. Solution: Press the Pause button immediately to prevent slag from splashing onto the focusing lens; Use oxygen as processing gas; Reduce feed rate; Increase power.
10.Imprecise cutting surface

Possible reasons: air pressure is too high; nozzle is damaged; nozzle diameter is too large; material is not good.
Solution: reduce air pressure; replace nozzle; install suitable nozzle; use material with smooth and uniform surface.
11.No burrs, the pull line is inclined, and the cut becomes narrower at the bottom

Possible cause: Feed rate is too high. Solution: Reduce feed rate.
12.Create crater

Possible reasons: air pressure is too high; feed rate is too low; focus is too high; rust on the plate surface; overheating of the workpiece being processed; impure material. Solution: reduce air pressure; increase feed rate; reduce focus; use better quality material (no rust, avoid overheating, ensure material purity).
13.Very rough cut surface

Possible causes: Focus too high; Air pressure too high; Feed rate too low; Material too hot. Solution: Lower the focus; Reduce air pressure; Increase feed rate; Cool the material.
Common Problems of Stainless Steel High Pressure Nitrogen Cutting and Laser Cutting:Stainless steel: Cutting with N2 high pressure
1.Produce small regular burrs in the shape of drops

When stainless steel is cut with N₂ high pressure, various defects often occur. If tiny regular burrs in the shape of drops are produced, it is mostly because the focus is too low and the feed rate is too high. You need to raise the focus and reduce the feed rate.
2.Long irregular filamentous burrs are produced on both sides, and the surface of large plates is discolored

Long irregular filamentous burrs appear on both sides and the surface of large plates is discolored, which is often caused by low feed rate, high focus, low air pressure or overheating of the material. Increase the feed rate, reduce the focus, increase the air pressure and cool the material.
3.Long irregular burrs are produced only on one side of the cut edge

If there are long irregular burrs on only one side of the cutting edge, it may be that the nozzle is not centered, the focus is high, the air pressure is low or the speed is low. You need to center the nozzle, lower the focus, increase the air pressure and increase the speed.
4.Yellowing of cut edges
The yellowing of the cutting edge is due to the presence of oxygen impurities in nitrogen. High-purity nitrogen needs to be used to ensure cutting quality and reduce defects.
5.Plasma generation on a straight line section
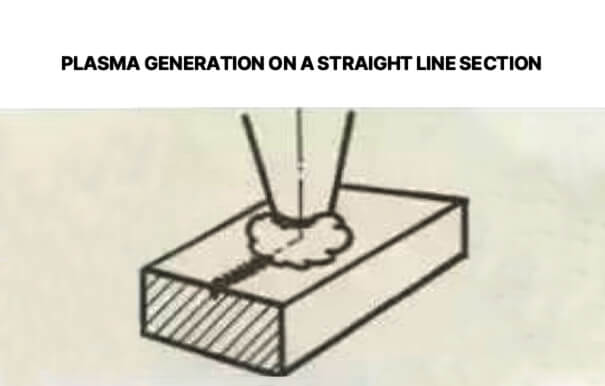
When plasma is generated on a straight section, it is because the feed rate is too high, the power is too low, and the focus is too low. At this time, press the pause button immediately to prevent the slag from splashing onto the focusing lens, then reduce the feed rate, increase the power, and raise the focus.
6.Beam Spread
If beam divergence occurs, the cause is also high feed rate, low power, and low focus. The solution is to reduce the feed rate, increase the power, and raise the focus.
7.Plasma generation at the corner
Plasma is generated at the corners due to large angle tolerance, too high modulation, and too high acceleration. The angle tolerance, modulation or acceleration needs to be reduced.
8.The beam diverges at the beginning
The light beam diverges at the beginning, which may be due to high acceleration, low focus or failure to discharge the molten material. The corresponding measures are to reduce the acceleration, raise the focus, and ensure that the molten material is discharged smoothly, so as to ensure the stability of the cutting process and improve the cutting quality.
9.Rough cut
When the cut is rough, if the nozzle is damaged, the nozzle needs to be replaced; if the lens is dirty, the lens needs to be cleaned and replaced if necessary.
10.Material is discharged from above

The material is discharged from the top, mainly because the power is too low, the feed rate is too high, and the air pressure is too high. In this case, press the pause button immediately to prevent the slag from splashing onto the focusing lens. Then increase the power, reduce the feed rate, and adjust the air pressure to ensure normal cutting.
Sobre nós
A Durmapress é especializada na conceção, fabrico e venda de vários equipamentos de processamento de metal, incluindo máquinas de dobragem, tesouras, punções, máquinas de corte a laser, etc. A empresa foi fundada em 2000. Com anos de experiência e acumulação de tecnologia. DurmaPress tornou-se uma das marcas bem conhecidas na indústria de máquinas de processamento de metal da China.
Contactar-nos
Publicações recentes
Categorias
Siga-nos
Novo vídeo semanal
Contacte-nos para mais informações
Se tiver alguma informação sobre os nossos produtos, contacte-nos e responderemos no prazo de 24 horas.


-300x169.jpg)


